|
Getting your Trinity Audio player ready...
|
Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) are useful tools for poverty eradication due to their contributions to job creation, economic growth, and empowerment of vulnerable populations.
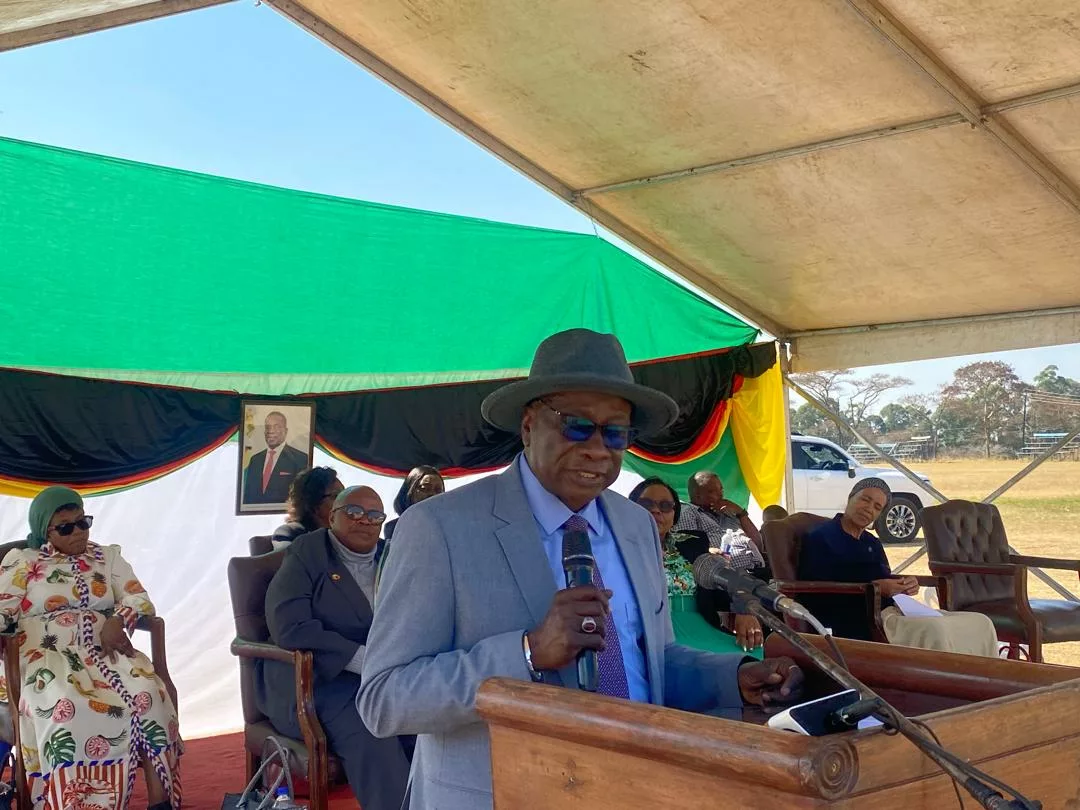
These were the sentiments of His Excellency Mr. Edward Kallon, the UN Resident and Humanitarian Coordinator in his remarks today at Chimhoyi University of Technology at the Commemoration of International Day of Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises held under the Theme: “Empowering MSMEs for a Resilient Future – Leveraging Power and Resilience of Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises to Accelerate SDGs and Eradicate Poverty in Times of Multiple Crisis.”
There were several dignitaries in attendance. Among them were Honourable Monica Mutsvangwa, Minister of Women Affairs, Community, Small, and Medium Enterprises Development; Honourable Marian Chombo, Minister of Provincial and Devolution Affairs for Mashonaland West; Honourable Dr. Jenifer Mhlanga, Deputy Minister of Women Affairs, Community, Small, and Medium Enterprises Development; Mavis Sibanda, Permanent Secretary of the Ministry of Women Affairs, Community, Small, and Medium Enterprises Development; Senior Government Officials; and representatives of the Zimbabwe Chamber of Small and Medium Enterprises.
“MSMEs are the backbone of economies globally. Their significant contributions to job creation, economic growth, and empowerment of vulnerable populations are undeniable. According to the International Labour Organization, MSMEs make up more than 90% of all businesses and account for a staggering 60 to 70% of employment and roughly 50% of global GDP (ILO, 2019). These figures alone underscore the profound impact of MSMEs in fostering economic resilience and sustainable development.
“The theme for this year’s commemoration, “Leveraging the Power and Resilience of MSMEs to Accelerate Sustainable Development and Eradicate Poverty in Times of Multiple Crises,” is not only timely but also critical. The world is facing unprecedented challenges, from economic instability to the impact of climate change such as the current El Nino induced severe drought and global pandemics. MSMEs have withstood the worst of these crises and continue to show remarkable resilience,” HE Kallon said.
In Zimbabwe, the story of MSMEs is a testament to resilience and innovation. Amidst economic downturns, hyperinflation, and a challenging business environment, MSMEs in Zimbabwe have continued to thrive, providing livelihoods, and fostering community development including in the informal sector.
He shared the story of Ms. Chipo (name changed for privacy), an entrepreneur from Harare whose small garment business nearly collapsed due to COVID-19. However, leveraging her ingenuity, she pivoted to producing face masks. Today, her business not only survived but expanded, employing more women in her community, and contributing to the local economy.
Despite their resilience, MSMEs in Zimbabwe face significant challenges. Chief among the challenges is limited access to finance: Only 41% of MSMEs in least-developed countries, including Zimbabwe, report access to finance as a major constraint (World Bank, 2020). Technological barriers are also a stumbling block. The lack of access to modern technology and digital tools inhibits productivity and global competitiveness.
MSMEs also face challenges in Market and Supply Chain Access. The restricted integration into global markets and supply chains limits their growth potential.
Regulatory and Administrative Burdens: also provide a nightmare for MSMEs. Complex regulations and high compliance costs add to MSMEs’ difficulties.
To harness the full potential of MSMEs and align their contributions with the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), HE Kallon said strategic interventions are required with the following policy recommendations:
Enhance Access to Finance:
- Developing Microfinance Institutions through the establishment and growth of microfinance institutions catering specifically to MSMEs’ needs is key.
- Financial Inclusion Programmes that provide MSMEs with affordable credit and comprehensive banking services is critical.
Promote Technology Adoption:
- Digital Transformation that includes supporting MSMEs in adopting digital technologies through training initiatives and subsidies is critical.
- There is need to improve ICT Infrastructure by investing in robust ICT infrastructure to facilitate MSMEs’ engagement in the digital economy.
Facilitate Market Access:
- Trade Facilitation by simplifying trade procedures and reducing barriers to market entry for MSMEs is important.
- There is a need to support Supply Chain Integration by fostering partnerships between MSMEs and larger firms to promote integration into established supply chains.
Regulatory Streamlining:
- Simplify Administrative Processes by streamlining the processes for business registration and compliance.
- One-stop shops through the establishment of centralized centers where MSMEs can access various government services efficiently.
To implement the above-outlined interventions, HE Kallon said the Government policymakers led by Honourable Mutsvangwa, with support from the United Nations family in Zimbabwe, have a pivotal role in creating an enabling environment for MSMEs. Key areas of intervention include:
Policy Advocacy and Development:
- Evidence-Based Policies: Formulating policies grounded in comprehensive data and evidence reflecting MSMEs’ needs is of paramount importance.
- Incentives for MSMEs like financial incentives such as tax breaks and subsidies to encourage MSME growth and formalization would go a long way.
Capacity Building and Support Programs:
- Design and implement Training and Development aimed at enhancing business acumen, technical skills, and resilience.
- Foster Mentorship and Networking programmes and networking opportunities to connect MSMEs with experienced professionals and peers.
Facilitating Innovation and Sustainable Practices:
- Promote Research and Development to advance MSMEs innovation and sustainable practices.
- Encourage MSMEs to adopt Circular Economy Integration principles to reduce costs, improve resource efficiency and contribute to tackling climate change, pollution and restoring biodiversity.
Improving Social Security and Labor Protections:
- Extending Legal Coverage including MSMEs in social security and labor legislation to provide workers with essential protections.
- Administrative Simplification through developing mobile or online registration systems to facilitate MSMEs enrolment in social security systems which requires a multi-sectoral and whole-government approach in line with the consistent mantra of His Excellency President ED Mnangagwa.
In this regard, the international community, including the United Nations, can provide crucial support by:
Funding and Financial Instruments through promoting strong collaboration with global financial institutions to create special funds and financial instruments for MSMEs support.
Knowledge Sharing and Capacity Building to offer technical assistance programmes to enhance capacity building and technology transfer.
Creating Inclusive Global Markets to facilitate trade partnerships and agreements that prioritize MSMEs inclusion in global value chains.
“As we commemorate MSME Day, I would like to renew the United Nations Development System’s commitment in Zimbabwe to fortify our support to the Government of Zimbabwe. Through collaborative efforts, we will uplift MSMEs to play their role in accelerating progress towards the SDGs and ensure that no one and no place is left behind. The resilience of MSMEs in Zimbabwe and around the world underscores their essential role in achieving sustainable development and eradicating poverty,” HE Kallon added.